Table Of Content

However, as the aspect ratio of a wing increases, it becomes more challenging to design the wing to have sufficient stiffness and strength without increasing its weight. As a result, a more extended wing is inevitably more flexible unless some additional structure is used to stiffen the wing. In the evolution of wings, airfoil sections have progressed from simple curved plate-like shapes with little thickness inspired by birds’ wings to sophisticated shapes with camber and thickness to give high lift and low drag. Airfoils used on subsonic airplanes are usually relatively thicker and have camber, as shown in the figure below.
Aircraft Wing Design: 10 Types of Aircraft Wings (Complete Guide)
There were a few bumps and blisters on top—notably the plexiglass bubble above the pilot’s position and a smaller one for the navigator to take sightings—but the crew nacelle, the fuel tanks, and bomb bays were inside the wing. It was thick enough, 85.5 inches at the root chord, to provide cramped cockpit space for a standard crew of nine. Additional contributions are greatly desired, especially 3-view drawings of unusualdesigns. Please email scans to Conceptual Research Corporationor mail them to CRC at PO Box 5429, Playa del Rey, CA 90296. This design is typically used to reduce the over length of the wing-mounted undercarriage legs while also raising the main fuselage. Other firms tried trapezoidal wings, or ones that approximated an ellipse with two or three trapezoidal panels, and found them not noticeably inferior to the elliptical.
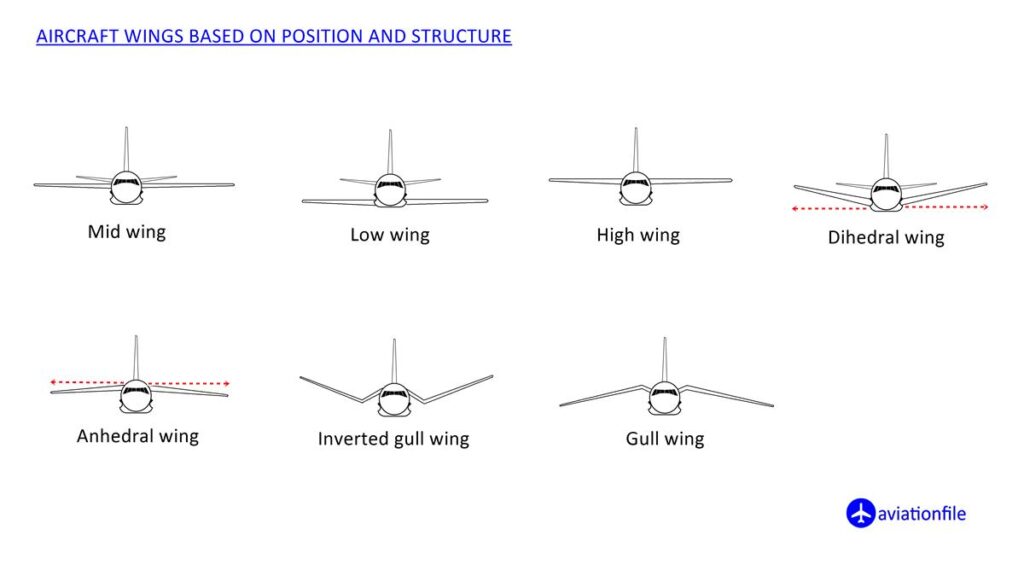
Anhedral wings are an interesting wing design
The Cessna 172 wing has an aspect ratio of 7.32 while the Dash 8 has a much higher aspect ratio of 12.78. Below is plot of the variation of wing loading (x-axis) with cruise speed (y-axis). Wing Area and Aspect Ratio are primary considerations when designing a subsonic aircraft (everything from a C172 to the Dash 8 Q400 shown above). Sweeping the wings becomes important once the aircraft begins to approach transonic and supersonic speeds (B747 and Mirage 2000).
NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars
Airfoils can come with all kinds of combinations of camber and thickness distributions. This slide gives technical definitions of a wing’s geometry, which is one of the chief factors affecting airplane lift and drag. The terminology used here is used throughout the airplane industry today and was mostly known to the Wright brothers in 1900.
The wing chord is the distance from its leading edge to its trailing edge in the streamwise direction, i.e., parallel to the airplane’s longitudinal axis. On many airplanes, the chord changes along the wing’s span, i.e., as in the above figure, mainly for aerodynamic reasons. A primary aerodynamic goal for the wing is minimizing drag for a given amount of lift, i.e., maximizing the lift-to-drag ratio. For the moment we are just going to focus on the relationship between velocity and the drag components. Looking at the induced drag line, you will notice that it decreases exponentially with velocity.
This New Blended-Wing Jetliner Was Just Cleared for Test Flights - Robb Report
This New Blended-Wing Jetliner Was Just Cleared for Test Flights.
Posted: Wed, 27 Mar 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The Wrights developed the final geometry for their wings by testing small models in their wind tunnel in 1901. They used mechanical balances to measure the lift and drag for their wing models. High aspect ratio wings have long spans (like high performance gliders), while low aspect ratio wings have either short spans or thick chords (like the Space Shuttle).
of the Most Common Wing Designs Used In the Aviation World
A triplane has three wings, a biplane two, and a monoplane the most common configuration in use today, has a single primary lifting surface. As shown in the images below, many different variations of winglets have been used on commercial airliners. Today, the trend is toward using more blended winglets with smooth chord variations in the wing-to-winglet transition area, which helps minimize the profile drag while maximizing induced drag reductions.
Together these deflections generate a rolling moment which forces the right wing up, and the left wing down. A better gauge of the relative size of the wing is the wing loading which is calculated by dividing the aircraft mass by the wing area. A wing is not designed to produce an equal upward force at all points along the span but rather produces the greatest percentage of the total lift closer to the root, diminishing outwards towards the span. The aspect ratio of a wing is important in aerodynamic analysis because a wing with a higher aspect ratio is generally more aerodynamically efficient and will have lower drag. The taper ratio may also be used in cases where the wing is not precisely linearly tapered to quantify the average taper of the wing planform.

About NASA
Truman liked it, too, and reportedly said, “This looks pretty damn good to me. I think we ought to buy some.” At his instruction, the YB-49 was flown down Pennsylvania Avenue and past the Capitol, but the President’s impressions were momentary and the budget cuts held. On June 5, 1948, a YB-49 broke up in flight over the Mojave Desert near Muroc Dry Lake in California, killing all five members of the test crew. The cause of the mishap was disputed, but structural failure almost certainly figured into it. The prospects for the Flying Wing were restructured in September 1948 with an Air Force contract for 30 YRB-49s in a reconnaissance variant called the RB-49A.
Its wingspan can be changed from straight to swept back, and vice versa, during flight. This alteration of shape allows for greater control and aerodynamic efficiency. The elliptical wing is aerodynamically most efficient because elliptical spanwise lift distribution induces the lowest possible drag.
It seems unlikely, however, that further reductions in induced drag can be realized by yet more permutations of the basic winglet design. Sailplanes, which are high-performance gliders, typically have very high aspect ratio wings compared to powered aircraft, so they can achieve high lift-to-drag ratios and can glide long distances by design. The DG-800 in the photograph below exemplifies a modern sailplane with an aspect ratio of just over 27. These types of sailplanes may be able to glide more than 50 miles (in still air) from an altitude of only 5,000 feet. Low aspect ratio wings will be short and fat, while high aspect ratio wings are long and thin. Most aircraft wings are not perfectly rectangular and so a little manipulation is required to formulate a convenient equation to calculate the aspect ratio quickly and easily.
That was the sound barrier, which aeronautical engineers figured out how to breach in 1947. However, flying near the speed of sound — around 660 mph at cruising altitudes, depending on air pressure and humidity — remained highly inefficient because of the drag caused by these standing shock waves. A wing is comprised of four principle structural components that work together to support and distribute the aerodynamic forces produced during flight.
The Beech Baron and the Cessna 210 are both six place high performance general aviation aircraft. The Cessna 210 has a single piston engine while the Beech Baron is a twin. They have an almost identical wing loading but the twin-engine configuration of the Baron means that it is slightly heavier, and as a result has a slightly larger wing in order to carry that extra weight. Before the structural layout of the wing is designed, a preliminary sizing of the wing planform should have been completed to size the wing for its required mission.

No comments:
Post a Comment